Why Some Dogs Have Longer Hind Legs Than Front Legs
Ever noticed some dogs with back legs longer than their front ones? It’s a common feature in certain breeds. This post delves into why this happens, touching on breed tendencies, anatomy, evolution, and breeding factors.
We’ll also examine how this trait affects movement and physical abilities, and provide care tips for such dogs. If you’ve pondered over your dog’s unique stance, let’s uncover this intriguing aspect together!
Key takeaways
Some dogs have longer back legs due to breed tendencies, anatomy, evolution, and breeding factors.
This unique characteristic can affect a dog’s movement, physical abilities, and potential health issues.
Dogs with longer back legs often exhibit superior agility, power, and speed.
Proper care, nutrition, and exercise tailored to these breeds can support their health and well-being.
Each dog is unique, and their individual traits should be embraced and celebrated.
Breeds with longer back legs
Overview of common dog breeds with longer back legs
While not every dog breed exhibits the characteristic of longer back legs, there are several breeds where this feature is more pronounced. These breeds often have unique body structures, and the longer back legs play a role in their overall appearance, function, and agility.
Let’s take a look at some examples of dog breeds with longer back legs.
Specific examples of breeds with this characteristic
Dachshunds
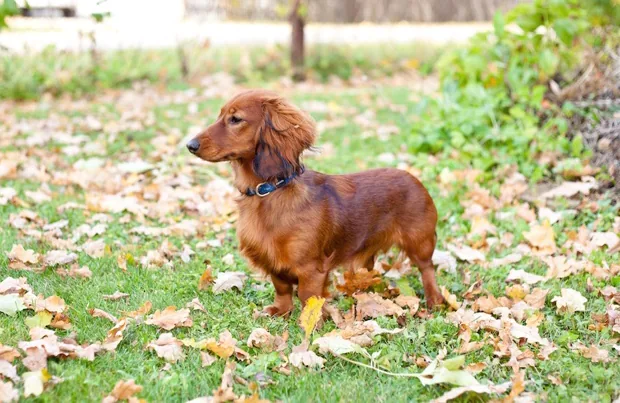

Dachshunds, often referred to as “wiener dogs,” are known for their elongated bodies and short legs. Despite their overall short stature, their back legs are slightly longer than their front legs.
This distinctive feature was originally bred into the Dachshund to help them burrow into tunnels and navigate tight spaces when hunting badgers and other small animals.
Basset Hounds

Another breed famous for its unique body structure is the Basset Hound. With a low-slung body and droopy ears, Basset Hounds also possess longer back legs compared to their front legs.
This breed was developed for scent tracking and needed a sturdy structure to support their large head and powerful nose. The longer back legs provide additional support and stability, enabling them to efficiently track scents without tiring easily.
Labrador Retrievers
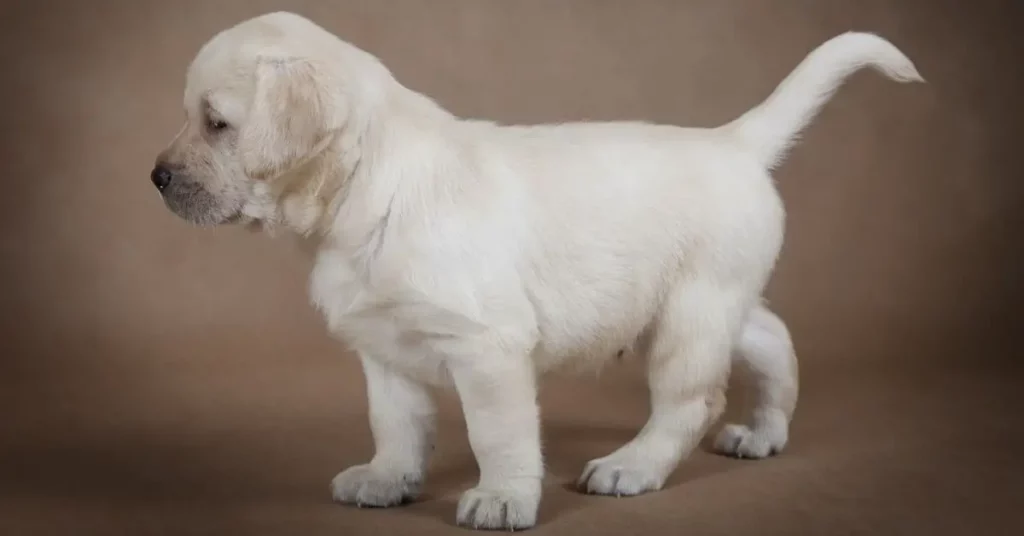

Labrador Retrievers, one of the most popular dog breeds worldwide, also exhibit a slightly longer back leg structure. Bred as working dogs, Labs were initially used for retrieving game during hunting. Their longer back legs offer them increased power and agility, making them excellent swimmers and efficient retrievers on land.
Greyhounds
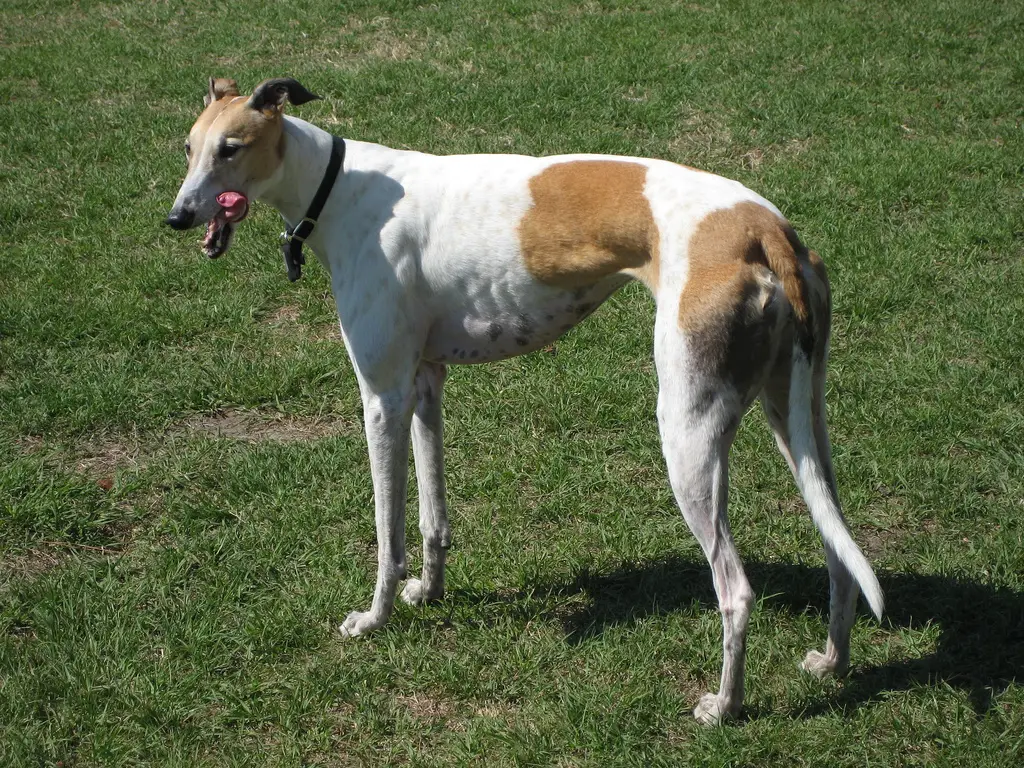

Greyhounds are well-known for their incredible speed and sleek body structure. Their longer back legs play a crucial role in providing them with the power and acceleration needed to reach high speeds in a short time.
This feature, combined with their lean bodies and deep chests, enables Greyhounds to excel in sprinting and chasing activities.
These are just a few examples of dog breeds with longer back legs than front legs. In the following sections, we will dive deeper into the anatomical differences and reasons behind this unique trait.
Anatomical differences
The role of skeletal structure
The skeletal structure of a dog plays a significant role in determining the length of their legs. Factors such as the slope of the croup and topline, as well as the angulation of the hip and shoulder joints, contribute to the appearance of longer back legs in some breeds.
Sloping croups and toplines
The croup is the region of a dog’s back that stretches from the base of the spine to the tail. In some breeds, like the Greyhound, a sloping croup and a curved topline contribute to the perception of longer back legs.
This unique skeletal structure allows for greater flexibility and range of motion, enhancing the dog’s agility and speed.
Angulation of the hip and shoulder joints
The angles at which the hip and shoulder joints are positioned also play a part in creating the appearance of longer back legs. Breeds with a higher degree of angulation in their hip joints tend to have longer back legs, as this allows for increased power and propulsion during movement.
On the other hand, a more upright shoulder joint may cause the front legs to appear shorter.
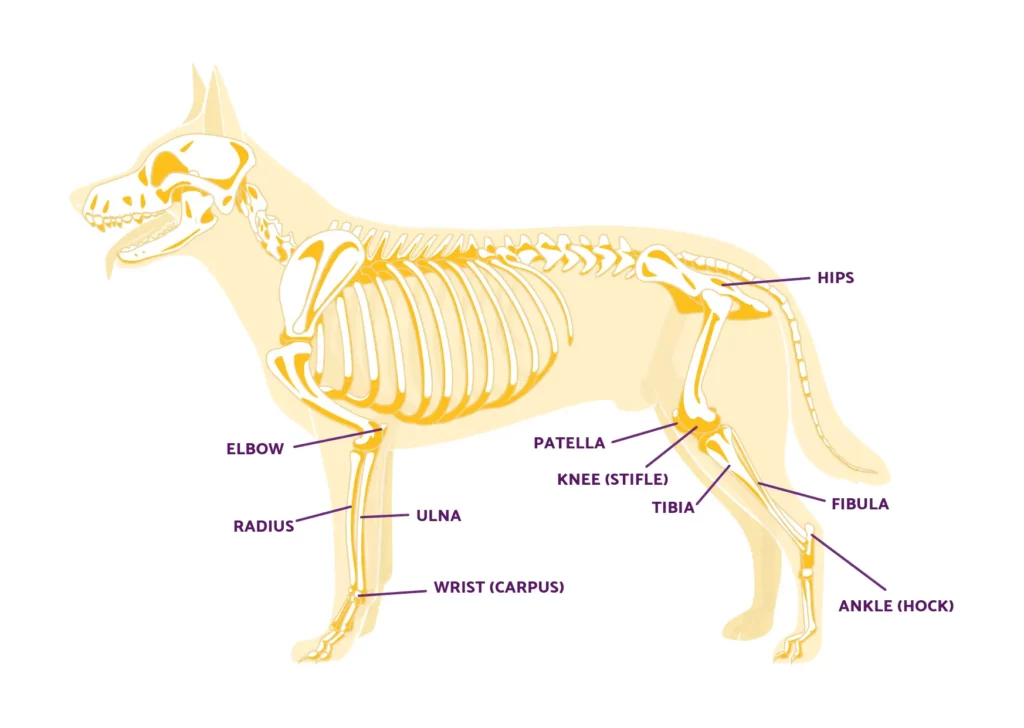
Musculature and its influence on leg length
In addition to the skeletal structure, the musculature of a dog also contributes to the perception of longer back legs. The development of specific muscle groups in the hind legs and forelegs can influence leg length and overall body shape.
Hind leg muscles
Dogs with longer back legs often have well-developed muscles in their hindquarters, such as the gluteal, hamstring, and quadriceps muscle groups. These muscles provide power and strength for activities like running, jumping, and swimming.
As a result, breeds with longer back legs typically excel in activities requiring bursts of speed or powerful movement.
Foreleg muscles
In contrast, the muscles in the front legs play a crucial role in providing stability and support for the dog’s body weight. While the foreleg muscles might not be as pronounced as the hind leg muscles, they still contribute to the overall balance and strength of the dog.
In some breeds with longer back legs, the front legs might appear shorter due to the difference in muscle mass and development compared to the hind legs.
Understanding the interplay between a dog’s skeletal structure and musculature is key to comprehending why some breeds have longer back legs than front legs. In the next sections, we will explore the evolutionary and breeding factors that have contributed to the development of this unique trait.
Evolutionary and breeding factors
Natural selection in wild canines
The leg length in dogs can be attributed, in part, to the process of natural selection. Wild canines have adapted over time to perform specific functions in their natural habitats, which in turn has influenced their leg length.
Running and endurance
Longer back legs are advantageous for canines that rely on running and endurance in their daily lives. For example, wolves and coyotes, which are ancestors of modern domestic dogs, have longer back legs compared to their front legs.
This anatomical feature allows them to cover long distances with ease and maintain their speed and stamina while hunting or traveling.
Leaping and hunting abilities
In addition to running and endurance, longer back legs also contribute to enhanced leaping and hunting abilities. Wild canines need to be agile and swift to catch their prey, and the powerful hindquarters of dogs with longer back legs provide them with the necessary strength and acceleration.
Selective breeding in domestic dogs
In domestic dogs, the leg length differences can also be attributed to the process of selective breeding. Breeders have carefully selected and bred dogs for specific functions or aesthetic preferences, resulting in breeds with longer back legs than front legs.
Working and sporting breeds
Working and sporting breeds, such as Labrador Retrievers and Greyhounds, were bred to excel in tasks that require agility, speed, and power. Longer back legs provide these breeds with the necessary physical characteristics to perform their intended functions, whether it be retrieving game, herding livestock, or racing.
Aesthetic preferences and breed standards
In some cases, breeders have focused on creating dogs with unique appearances, resulting in breeds with pronounced leg length differences, such as Dachshunds and Basset Hounds.
These aesthetic preferences have been standardized within breed clubs and organizations, ensuring that the breed’s distinct characteristics are preserved and maintained over time.
In summary, the leg length differences in dogs can be traced back to a combination of evolutionary and breeding factors that have shaped each breed’s unique characteristics and functions.
In the following sections, we will discuss how longer back legs impact a dog’s movement and physical abilities, as well as the importance of proper care for these breeds.
Effects on movement and physical abilities
Impact on locomotion
The length of a dog’s legs can have a significant impact on their overall movement and locomotion. Dogs with longer back legs exhibit unique movement patterns that are influenced by their anatomy.
Galloping and trotting
Dogs with longer back legs tend to have a more pronounced galloping gait, which allows them to cover more ground with each stride. This powerful, efficient movement is especially beneficial for breeds that excel in running and endurance activities.
Additionally, some breeds with longer back legs may display a unique trotting gait that enables them to move swiftly and smoothly over various terrains.
Jumping and climbing
Longer back legs also contribute to a dog’s ability to jump and climb. Breeds with this anatomical feature possess increased strength and power in their hindquarters, which enables them to leap higher and climb with more ease.
This can be particularly useful for breeds that are bred for tasks requiring agility, such as retrieving game or navigating challenging environments.
Potential health issues
While longer back legs offer several advantages in terms of movement and physical abilities, they can also be associated with certain health issues. It’s important for dog owners to be aware of these potential concerns and take appropriate preventive measures.
Hip dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a common condition in some dog breeds, in which the hip joint does not develop properly. This can lead to arthritis and pain, especially in breeds with longer back legs. Regular check-ups, proper exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of hip dysplasia in dogs.
Patellar luxation
Patellar luxation, or dislocation of the kneecap, is another condition that can affect dogs with longer back legs. This condition can cause discomfort and mobility issues if left untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, such as surgery or physical therapy, can help improve your dog’s quality of life.
Spinal issues
Some breeds with longer back legs may be more prone to spinal issues, such as intervertebral disc disease (IVDD), particularly in breeds with elongated bodies like Dachshunds. Regular veterinary care, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the spine can help prevent or manage these issues.
It’s essential to understand the impact of leg length on a dog’s movement and physical abilities, as well as potential health concerns. In the next section, we will provide tips on proper care for dogs with longer back legs to ensure they remain healthy and happy throughout their lives.
Proper care for dogs with longer back legs
Exercise recommendations
Importance of regular physical activity
Dogs with longer back legs benefit greatly from regular exercise, as it helps maintain their muscle tone, joint health, and overall well-being. Engaging your dog in activities tailored to their breed and individual needs can ensure they remain fit and healthy.
Suitable exercises for different breeds
Each breed may require different types of exercise to accommodate their unique anatomy and capabilities. For example, Labrador Retrievers enjoy swimming and retrieving activities, while Greyhounds thrive with short bursts of sprinting.
It’s essential to consult with your veterinarian to determine the most appropriate exercise regimen for your dog’s breed, age, and physical condition.
Nutritional considerations
Proper diet for maintaining healthy joints
A balanced diet is crucial for all dogs, but it is particularly important for those with longer back legs. Nutrients such as glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids can help maintain joint health and prevent issues like hip dysplasia. Consult your veterinarian to select the best diet for your dog’s specific needs.
No products found.
Importance of weight management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for dogs with longer back legs, as excess weight can put additional strain on their joints and spine. Regular exercise, portion control, and choosing the right food can help keep your dog at an optimal weight and reduce the risk of health issues related to their unique anatomy.
Preventative healthcare
Regular check-ups
Routine veterinary check-ups are crucial for dogs with longer back legs, as they can help detect and address potential health issues early. Your veterinarian can also provide guidance on exercise, diet, and any necessary preventive measures tailored to your dog’s breed and individual needs.
Screening for potential genetic disorder
Some breeds with longer back legs may be prone to specific genetic disorders. Early screening through genetic testing can help identify any predispositions your dog may have, allowing you to take appropriate preventive measures and seek timely treatment if needed.
Taking proper care of a dog with longer back legs involves a combination of appropriate exercise, a balanced diet, and regular veterinary care. By addressing these aspects, you can ensure that your furry friend remains healthy and happy, while also enjoying their unique physical abilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it normal for my dog’s back legs to be longer than the front legs?
Yes, it is normal for some dog breeds to have longer back legs than front legs due to their breed’s specific anatomy, evolution, and breeding factors.
Can uneven leg length cause health issues in dogs?
While uneven leg length can sometimes be associated with health issues such as hip dysplasia, patellar luxation, or spinal problems, proper care and regular veterinary check-ups can help to minimize risks and address issues as they arise.
How can I tell if my dog’s leg length difference is normal or a health concern?
If you are unsure whether your dog’s leg length difference is normal or indicative of a health concern, consult your veterinarian. They can assess your dog’s overall health, perform necessary tests, and provide appropriate advice based on your dog’s breed and individual needs.
Do dogs with longer back legs require special care or treatment?
While dogs with longer back legs may not require specific treatment, they may benefit from certain exercise types, a healthy diet, weight management, and regular check-ups to help maintain joint health and reduce the risk of health issues related to their unique anatomy.
Final Thoughts
We’ve delved into why some dogs have longer back legs, covering breed tendencies, anatomy, evolution, and breeding. We’ve also looked at how this affects movement, abilities, and health, offering care tips for these dogs.
Understanding this can help you appreciate their uniqueness and provide tailored care. Embrace your dog’s individual traits and celebrate their agility, power, and speed. After all, these traits make them a one-of-a-kind companion.







